What is “New Digital Jukebox” (New DJ)?
New Digital Jukebox is an audiovisual generative structure that was created as part of the “Generative Design” seminar at the TH Brandenburg. The centerpiece is the “baton”, a rod attached to a ball head. By attaching it to a ball head, the baton can be tilted in different directions and also fixed in place. Alternatively, it can also be held freely in the hand. A generative composition system can be controlled by tilting the rod. In this way, moods of different genres can be generated and mixed to create interesting sound compositions. The user thus becomes a conductor. This composition is supported by a visual level, which is controlled by both the rod and the music.
How did the name come about?
The name of the installation is based on the jukeboxes from the 20th century, where you could choose from different titles by inserting a coin. A jukebox was often adorned with lights, which matches the visual level of the installation. New Digital Jukebox can be abbreviated to New DJ, which is also a reference to the disc jockey. The baton can be used to switch smoothly between the different genres, just like in DJing.
How does New DJ work?
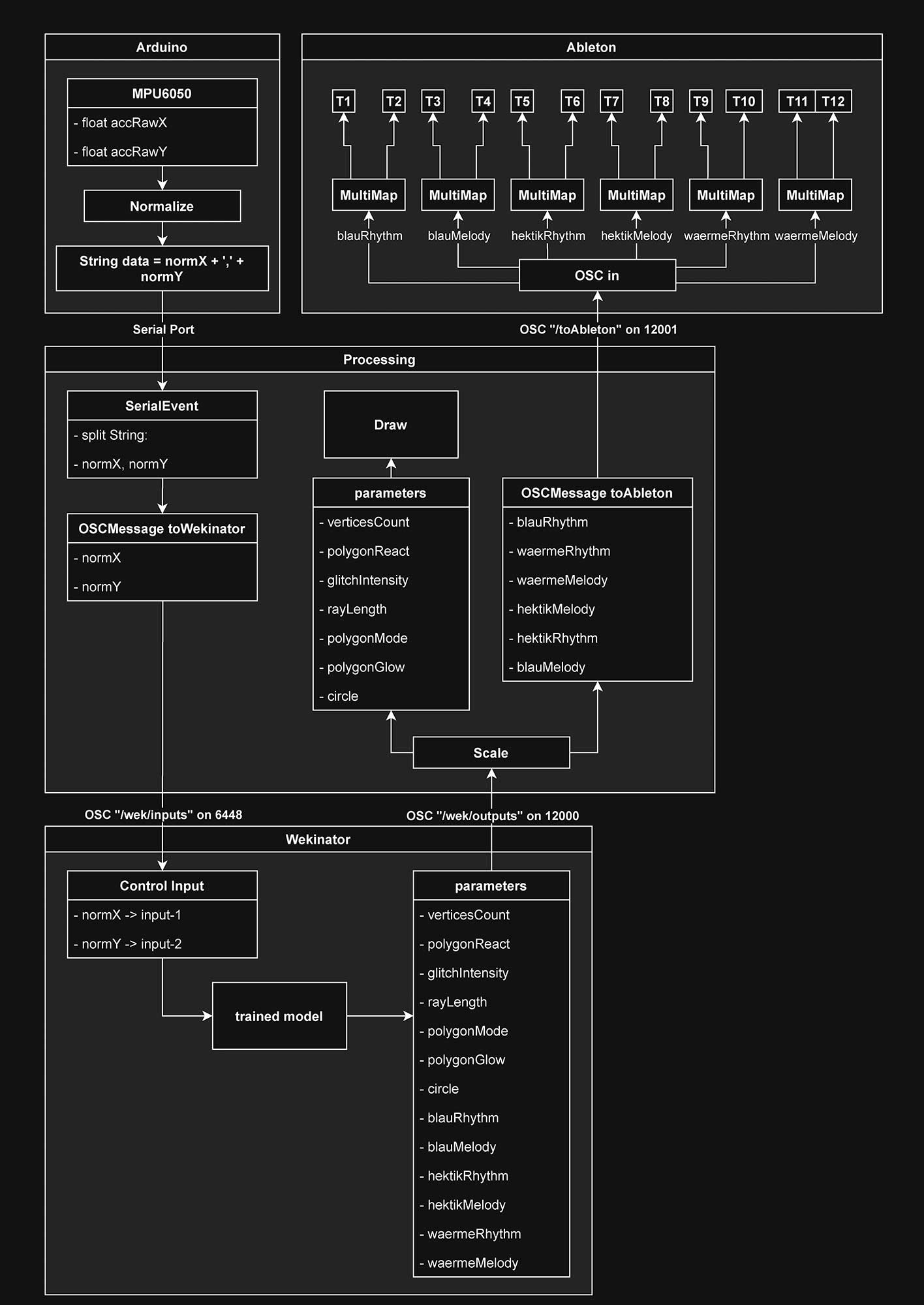
New DJ is a synthesis of different software and tools. To give you a rough overview, here is a short list of which tools were used for which purpose:
Arduino
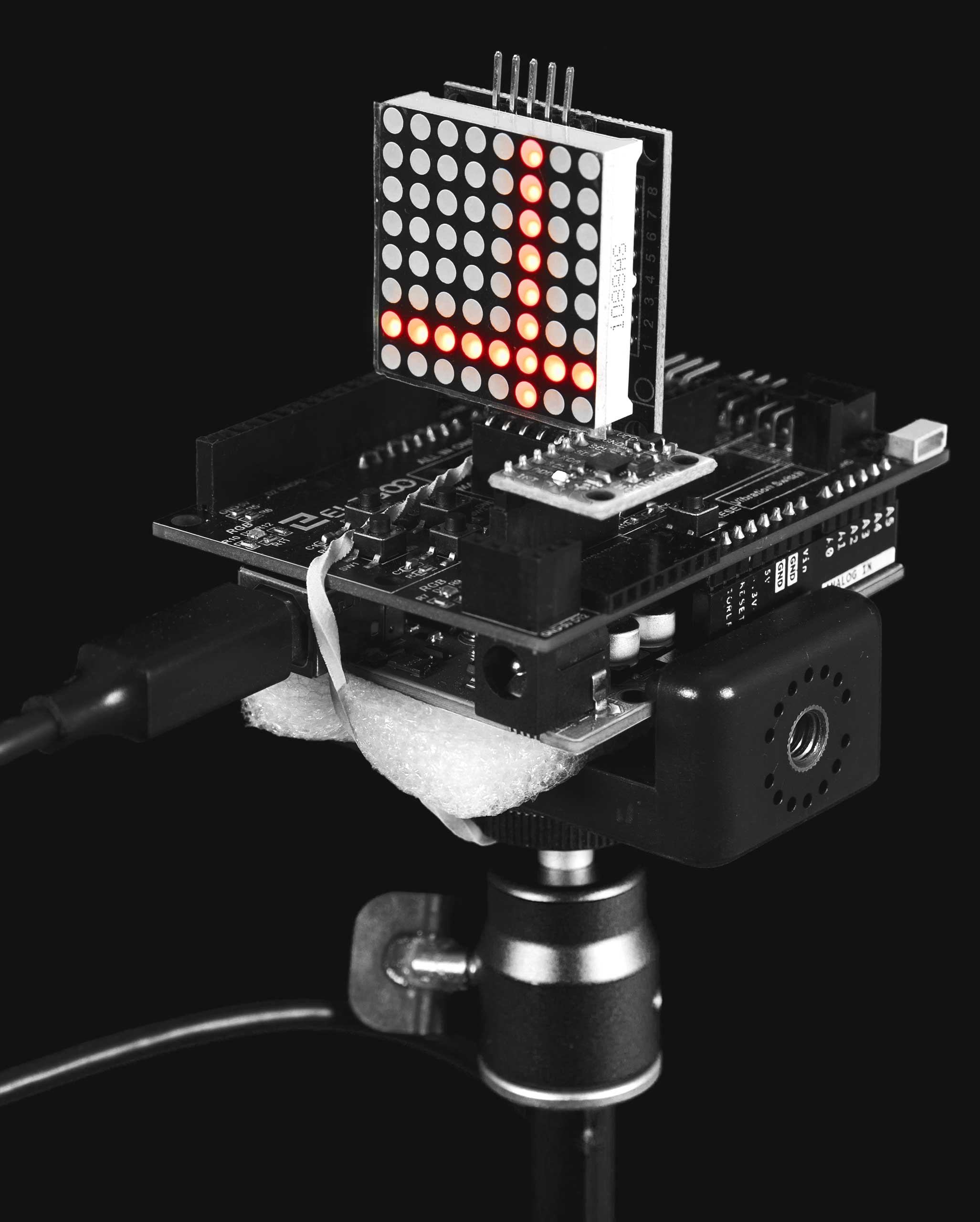
An Arduino Uno is used as the input device. An accelerometer (MPU6050) is connected to this and its X and Y values are used as input values. An LED matrix serves as visual feedback for the inclination of the axes. The values are normalized and transmitted to Processing via the serial port.
Wekinator
With the help of Wekinator, an open source tool, a trained model was created using supervised machine learning. This model uses the inclination to control numerous parameters that are responsible for controlling the composition system and for visualization.
Processing
The Processing programming language is used for visualization. Processing is also used as the central communication interface between the applications. Open Sound Control (OSC) and the serial port are used.
The visualization reacts to a large extent to the music. To this end, the music is broken down into its individual frequency components using Fast Fourier Transform (FFT). For example, beat detection can be implemented or individual elements only react to certain frequency components.
Ableton Live
Ableton Live is used as the DAW for the music. The instrumentation is carried out in Ableton. Furthermore, tracks are provided with effects and the mix is realized. Ableton Live offers the advantage of integrating Max/MSP, a graphical development environment.
Max for Live
Patches generate melodies and rhythms in real time using algorithms that receive both preset and live modifiable parameters as input values. In combination with random values, unique melodies are created. The sequence and length of the piece can be freely controlled, whereby each run is never the same as the next.